Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
OP18: Proactive adalimumab trough measurements increase corticosteroid-free clinical remission in pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease: The pediatric Crohn's disease adalimumab level-based optimization treatment (PAILOT) trial
2019
ECCO'19 Copenhagen
Tuesday, 28 May 2019, 3:32 PM
1
OP18: Surgical prevention of anastomotic recurrence by excluding mesentery in Crohn's Disease: The SuPREMe-CD Study
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP18: Surgical prevention of anastomotic recurrence by excluding mesentery in Crohn's Disease: The SuPREMe-CD Study
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 4:58 PM
1
OP18: Treatment of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical closure after anti-TNF induction treatment versus anti-TNF without surgery (PISA II) - A patient preference RCT
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Wednesday, 2 June 2021, 4:12 PM
OP18: Treatment of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical closure after anti-TNF induction treatment versus anti-TNF without surgery (PISA II) - A patient preference RCT
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP19 Perinatal factors do not affect paediatric inflammatory bowel disease risk: A Scottish Nationwide Cohort study using administrative health data 1981–2017
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Thursday, 30 January 2020, 10:12 AM
OP19: Classifying perianal fistulising Crohn’s Disease: An expert-consensus to guide decision-making in daily practice and clinical trials
2022
ECCO'22
Friday, 11 February 2022, 3:52 PM
OP19: Corticosteroid response rectal gene signature and associated microbial variation in treatment naïve ulcerative colitis
2019
ECCO '19 Copenhagen
Friday, 22 February 2019, 9:41 AM
OP19: Corticosteroid response rectal gene signature and associated microbial variation in treatment naïve ulcerative colitis
2019
ECCO'19 Copenhagen
Tuesday, 28 May 2019, 3:32 PM
1
OP19: Disease course and treatment outcomes of early resected Crohn's Disease patients: A Danish nationwide cohort study from 1997 to 2015
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Wednesday, 2 June 2021, 4:12 PM
OP19: Disease course and treatment outcomes of early resected Crohn's Disease patients: A Danish nationwide cohort study from 1997 to 2015
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP19: Extended mesenterectomy is not superior to mesenteric sparing resection in primary ileocolic resection for Crohn’s Disease in terms of postoperative endoscopic recurrence – results of an international randomised controlled trial
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP19: Gaps between ECCO quality standards of care and the real world: the E-QUALITY survey
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP19: Gaps between ECCO quality standards of care and the real world: the E-QUALITY survey
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 10:43 AM
OP19: Perinatal factors do not affect paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease risk: A Scottish nationwide cohort study using administrative health data 1981-2017
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP19: Perinatal factors do not affect paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease risk: A Scottish nationwide cohort study using administrative health data 1981-2017
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 4:58 PM
1
OP20 The gut microbiota during biological therapy for inflammatory bowel disease
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Thursday, 30 January 2020, 10:12 AM
OP20: Mucosal micoRNA profiles predict response to autologous stem-cell transplantation in Crohn’s disease
2019
ECCO '19 Copenhagen
Friday, 22 February 2019, 9:41 AM
OP20: Mucosal microRNA profiles predict response to autologous stem-cell transplantation in Crohn’s Disease.
2019
ECCO'19 Copenhagen
Tuesday, 28 May 2019, 3:32 PM
1
OP20: Perianal fistulas are characterised by expansion of interleukin-22 producing invariant natural killer T-cells and CD4+ T-cells which drive dysregulation of the extracellular matrix
2022
ECCO'22
Friday, 11 February 2022, 3:52 PM
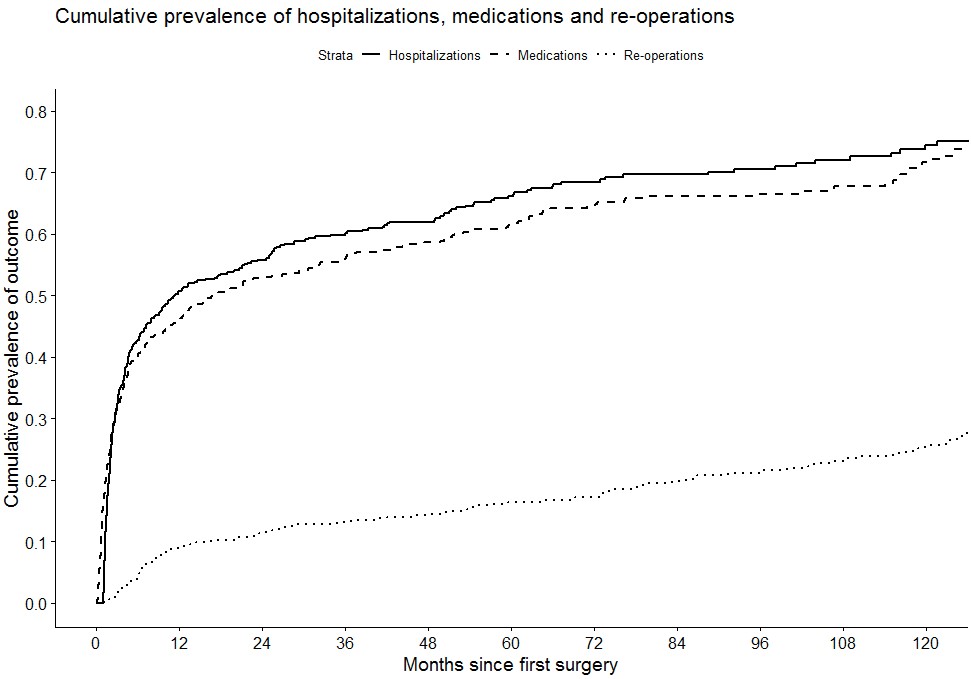
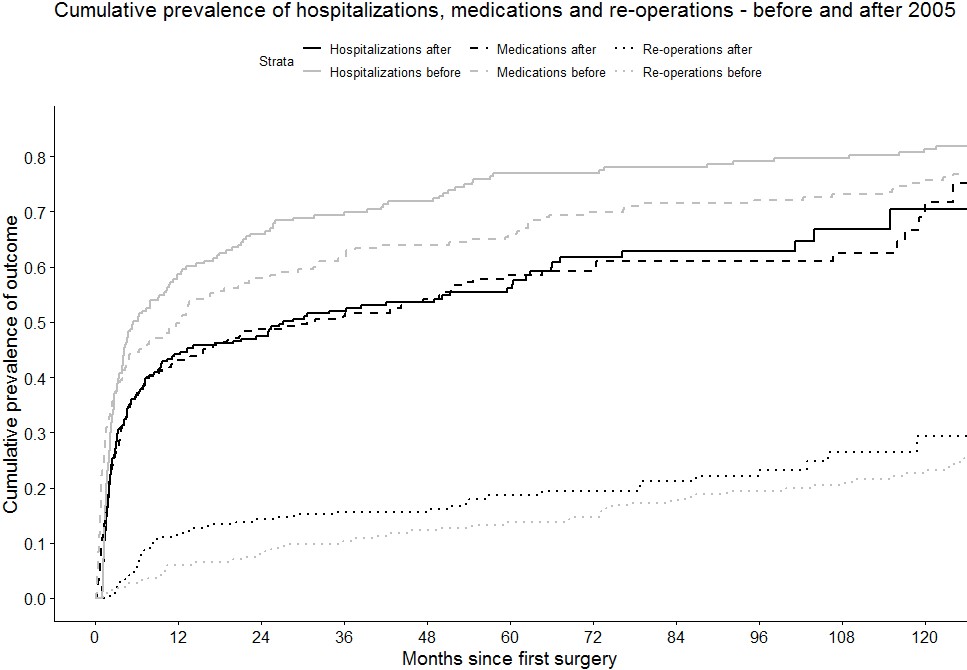 Conclusion
Conclusion