Predictors of response to anti-TNF therapy - not the usual -omicsYear: 2020
Source: JCC Podcast
Authors: John Nik Ding
Created: Tuesday, 13 October 2020, 3:58 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Last Modified: Tuesday, 13 October 2020, 4:00 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Dr John Nik Ding reports his study of urine, faecal and serum metabonomic and microbial predictors of response to anti-TNF therapy in 76 Crohn’s patients.
PregnancyYear: 2022
Source: 20th IBD Intensive Course for Trainees
Authors: Iris Dotan; Janneke van der Woude
Created: Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Summary contentLearning Objectives:
1. Pre conception counseling, optimal disease control, planning, adherence
2. Drug safety at conception and during pregnancy
3. Management of disease exacerbation during pregnancy, assessment and therapeutic options
4. Management of biologics during pregnancy and post-partum
5. Multidisciplinary decision concerning through the entire pregnancy and important decision like mode of delivery
Pregnancy in IBDYear: 2017
Source: Educational Audio Podcast
Authors: Pascal Juillerat
Created: Friday, 28 February 2020, 11:10 AM by Dauren Ramankulov
Last Modified: Monday, 17 August 2020, 10:57 AM by Dauren Ramankulov
Pregnancy, IBD, and COVID-19 - what you need to knowYear: 2020
Source: JCC Podcast
Authors: Alison de Lima and Janneke van der Woude
Created: Wednesday, 10 March 2021, 2:06 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Alison de Lima and Janneke van der Woude discuss their article summarising the available evidence on the management of pregnancy in IBD in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Prevention and Management of Infections in IBD Year: 2021
Source: e-Course
Authors: Stephan Vavricka, Julien Kirchgesner, Thomas Greuter, Bram Verstockt
Created: Wednesday, 10 March 2021, 1:51 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Last Modified: Wednesday, 10 March 2021, 1:53 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Upon completion of this case you will:
- Define which infectious tests (serology, PCR, cultures, …) should be performed at IBD diagnosis, prior to biological/small molecule therapy or while flaring
- Monitor IBD patients with previous hepatitis B virus infection
- Treat Clostridium difficile infection
- Advise IBD patients who want to travel
- Advise pregnant or breastfeeding IBD patients on vaccination
Prevention initiativesYear: 2020
Source: ECCO'20 Vienna
Authors: Jean-Frédéric Colombel
Created: Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
Prevention initiativesYear: 2020
Source: ECCO'20 Vienna
Authors: Jean-Frédéric Colombel
Created: Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 4:58 PM
Files: 1
Primary sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinomaYear: 2021
Source: 6th H-ECCO IBD Masterclass
Authors: Francesca Rosini
Created: Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
Summary contentPrimary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) is a chronic and progressive cholestatic disease, characterised by inflammation of the intrahepatic and/or extrahepatic bile ducts, progressive fibrosis and scarring of the liver parenchyma and eventually end-stage liver disease. About 70% of patients with PSC have underlying IBD, most frequently ulcerative colitis (UC). Conversely, in patients with known IBD, PSC is found much less commonly, occurring in about 2% to 8% of UC patients and 3% of Crohn’s disease (CD). Despite initial enthusiasm for a genetic link in PSC-IBD, recent genomics data did not show a strong association. Inflammatory bowel disease coexisting with PSC has a specific behaviour and it is considered a distinct phenotype known as “PSC-IBD”. Prolonged duration of IBD is associated with an increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) in PSC patients.
-To have an overview on histological features of PSC.
-To understand the association between PSC and IBD.
-To understand the association between PSC and Cholangiocarcinoma.
-To learn features of cholangiocarcinoma.
Proactive TDM: Feasible? Reasonable?Year: 2022
Source: 8th ClinCom Workshop
Authors: Konstantinos Papamichail
Created: Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Summary contentSummary: Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) has emerged as a useful tool for optimizing biological therapy, and particularly anti-tumor necrosis factor (anti-TNF) therapy, in patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Growing evidence suggest that proactive TDM of anti-TNF therapy, with the goal of targeting a predefined drug concentration threshold, is associated with better therapeutic outcomes compared to standard of care. Proactive TDM can also be utilized when infliximab de-escalation is considered and following infliximab re-initiation after a drug holiday. However, there are still several challenges regarding the widespread utilization of proactive TDM in clinical practice including the identification of the optimal drug concentration to target. Future perspectives of proactive TDM of biologics include the implementation of model-informed precision dosing and pharmacogenetics towards personalized medicine.
Educational objectives:
- · To introduce the concept of therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of biologics
- · To review the data regarding the role of proactive TDM for optimizing biologics in IBD
- · To describe the potential applications of proactive TDM of biologics in IBD
- · To identify the knowledge gaps regarding utilization of proactive TDM of biologics in IBD clinical practice
- · To discuss the future perspectives of proactive TDM of biologics in IBD
Proactive Therapeutic Drug Monitoring is superior to standard treatment during maintenance therapy with infliximab; results from a 52-week multicentre randomised trial of 450 patients; the NOR-DRUM B studyYear: 2022
Source: ECCO'22 Virtual
Authors: Kristin Kaasen Jørgensen
Created: Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
BackgroundProactive therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), individualized treatment based on scheduled assessments of serum drug levels, has been proposed to optimize efficacy and safety of infliximab and other biologic drugs. However, it is unclear whether this strategy improves clinical outcomes.
MethodsIn this 52-week randomised, open-label, multicenter trial, adult patients with an established diagnosis of ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis (SpA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), and psoriasis (Ps) receiving infliximab therapy for a minimum of 30 weeks were randomly assigned to proactive TDM or standard infliximab treatment. In the TDM group, infliximab dosage was adjusted according to an algorithm designed to maintain serum infliximab levels within the therapeutic range 3-8 mg/L. In the standard treatment group, infliximab dosage was based on clinical judgement.The primary endpoint was sustained disease control during the 52 week study period.
ResultsIn total, 458 patients were randomised of whom 454 (UC 81, CD 66, RA 79, PsA 53, SpA 138, Ps 37) received the allocated strategy and were included in the primary analyses. The two groups were balanced regarding baseline demographics, clinical and treatment characteristics. Sustained disease control without disease worsening was observed in 167 (73.6 %) patients in the TDM group and in 127 (55.9%) patients in the standard treatment group. The estimated adjusted difference was 17.6% (95% confidence interval (CI), 9.0-26.2, p<0.001), favouring TDM (figure 1). Results were consistent in sensitivity analyses. Time to disease worsening was shorter in the standard treatment group, hazard ratio 2.1 (95% CI 1.5-2.9) (figure 2). Other secondary endpoints reflecting change in disease activity and patient reported outcomes from baseline to week 52 did not show significant differences between the two groups. During the trial, the mean infliximab dose (4.8 mg/kg) and median serum level of infliximab (5.8 mg/L) were comparable in both groups. Twenty-one (9%) patients in the TDM group and 27 (15%) in the standard treatment group developed clinically significant levels of anti-drug antibodies (≥50µg/L). Adverse events were reported in 137 (60%) and 142 (63%) patients in the TDM and standard treatment groups, respectively.
Figure 1

Figure 2
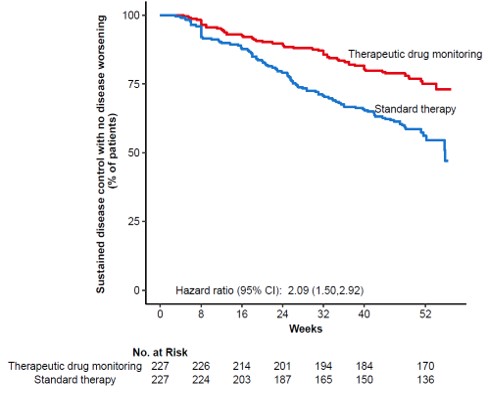
ConclusionThis large randomised controlled trial demonstrates that proactive TDM is superior to standard treatment for maintaining disease control without disease worsening in patients on maintenance therapy with infliximab. These results support implementation of proactive TDM as a general strategy during maintenance therapy with infliximab and have the potential to change clinical practice across specialities.
Problems around the anus (Tandem talk)Year: 2022
Source: 6th Basic ECCO: EduCational COurse for Industry
Authors: Antonino Spinelli; Silvio Danese
Created: Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Summary contentPerianal manifestation in Crohn’s disease patients is likely to complicate the disease course with extra intestinal manifestations, abscesses, deep anal canal ulcers, luminal fistulas and strictures, steroid resistance, and need for multiple surgeries. Diagnosis and management of perianal Crohn’s disease implies a multidisciplinary team approach. Diagnosis and definition of perianal disease requires optimal imaging modality, ideally a pelvic magnetic resonance imaging, with an exam under anesthesia (EUA). However, the lack of a definition consensus on perianal fistula in Crohn’s disease may affect standardization of therapeutic approaches and patients inclusion within clinical trial.
The synergic approach by a surgeon and a gastroenterologist is crucial with perianal Crohn’s disease. Drainage of an abscess and possible seton placement to prevent future septic complications is the basic first step of the treatemnt. Ani-TNF drug have shown the best evidence for decreasing perianal drainage and promote fistula healing. Attempting surgical repair is possibile for selected patients. Surgical strategies include subcutaneous fistulotomy, Ligation of the Intersphincteric Tract (LIFT) procedure, or endorectal advancement flap (ERAF). These surgical strategies work best when associated with anti-TNF or immunomodulation and when mild to moderate proctitis is present. More aggressive interventions include diversion of the fecal stream with loop ileostomy and proctectomy; Mesenchymal stem cells have emerged as possible effective treatment and long term results have been demonstrated by randomized clinical trial.

