Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
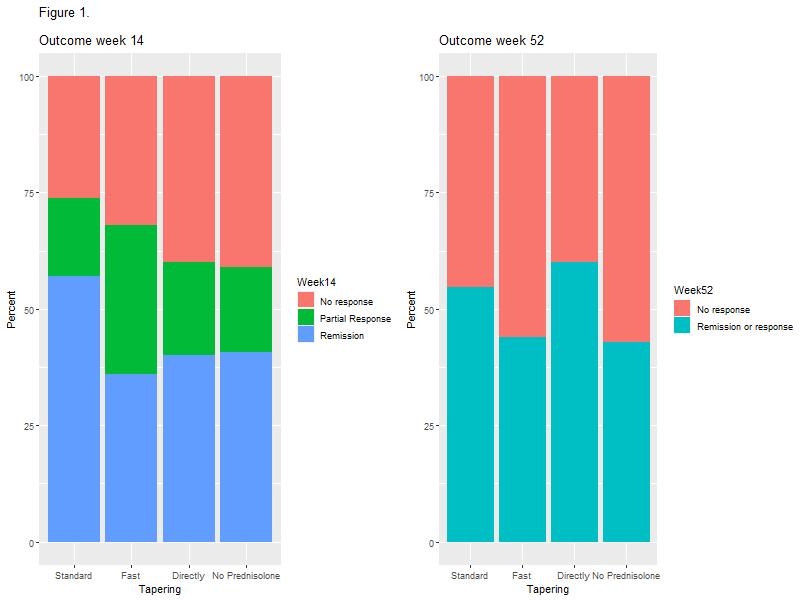
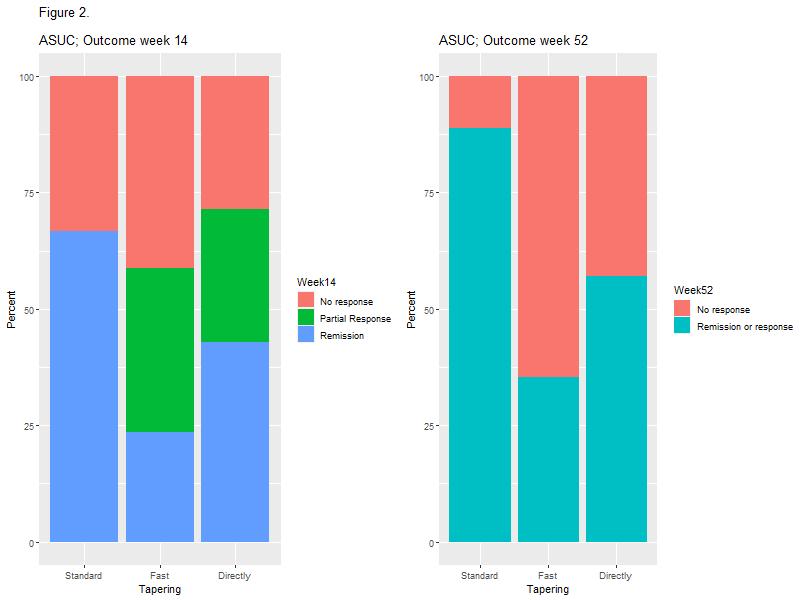
The influence of different prednisolone tapering algorithms on the effectiveness of infliximab in patients with Ulcerative Colitis – A real-world cohort study
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The long-term safety outside clinical trials
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:50 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The mesentery in ileocolic resection
2018
7th S-ECCO IBD Masterclass
Tuesday, 8 May 2018, 11:36 AM
1
The MIND study: Assessment of psychological characteristics and postop outcomes
2021
10th S-ECCO IBD Masterclass
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
The multi-refractory paediatric patients: Out of the box therapeutic treatments
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
The multi-refractory paediatric patients: Out of the box therapeutic treatments
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 4:58 PM
1
The nursing perspective of Quality Standards of Care
2020
14th N-ECCO Network Meeting
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 4:58 PM
1
The patient with psychological comorbidities: How to wean off opiates in these patients? Is there any preference in drugs?
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:18 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The PROmise of remote monitoring tools in IBD daily care (Tandem talk)
2020
5th EpiCom Workshop
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 4:58 PM
1
The pros and cons of using the GRADE vs Oxford methodology (M. González Lorenzo)
2019
1st Guideline Methodology and GRADE Workshop
Tuesday, 28 May 2019, 3:32 PM
1
The pros and cons of using the GRADE vs Oxford methodology (T. Lytras)
2019
1st Guideline Methodology and GRADE Workshop
Tuesday, 28 May 2019, 3:32 PM
1
The reproductive phase: Practical recommendations
2019
ECCO'19 Copenhagen
Tuesday, 28 May 2019, 3:32 PM
1
The reproductive phase: Practical recommendations
2019
Scientific Programme
Wednesday, 5 June 2019, 9:01 PM
The role of pharmacoepidemiology in regulatory agencies
2018
4th EpiCom Workshop
Friday, 23 March 2018, 12:23 PM
1