Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
ECCO ESPGHAN Guideline Pitch on Paediatric CD (update)
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
ECCO Fellowship presentation: Targeting CD4+ T-cell plasticity in IBD
2021
7th Y-ECCO Basic Science Workshop
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
ECCO Guidelines on Sexuality, Fertility, Pregnancy and Lactation
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
ECCO Guidelines on Ulcerative Colitis - Medical and Surgical Treatment
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
ECCO Guidelines: Prevention and management of Opportunistic Infections (Tandem Talk)
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
ECCO Lecture: IBD clinical trials: Where do we go from here?
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
ECCO Lecture: Inflammatory Cytokines from Discoveries to Therapies
2019
Scientific Programme
Wednesday, 5 June 2019, 9:01 PM
ECCO-ESGAR Guidelines: Present and future of diagnostic techniques for IBD
2018
ECCO'18 Vienna
Friday, 23 March 2018, 12:23 PM
Tuesday, 8 May 2018, 3:30 PM by Lindley Fritze
1
Effect of baseline disease characteristics on clinical outcomes in moderate-to-severe Ulcerative Colitis treated with upadacitinib: Results from a Phase 3 trials programme
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Effect of upadacitinib (UPA) treatment on extraintestinal manifestations (EIMs) in patients with moderate-to-severe Ulcerative Colitis (UC): Results from the UPA Phase 3 programme
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Effectiveness and Safety of tofacitinib versus vedolizumab in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis; A Nationwide, ICC Registry study
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
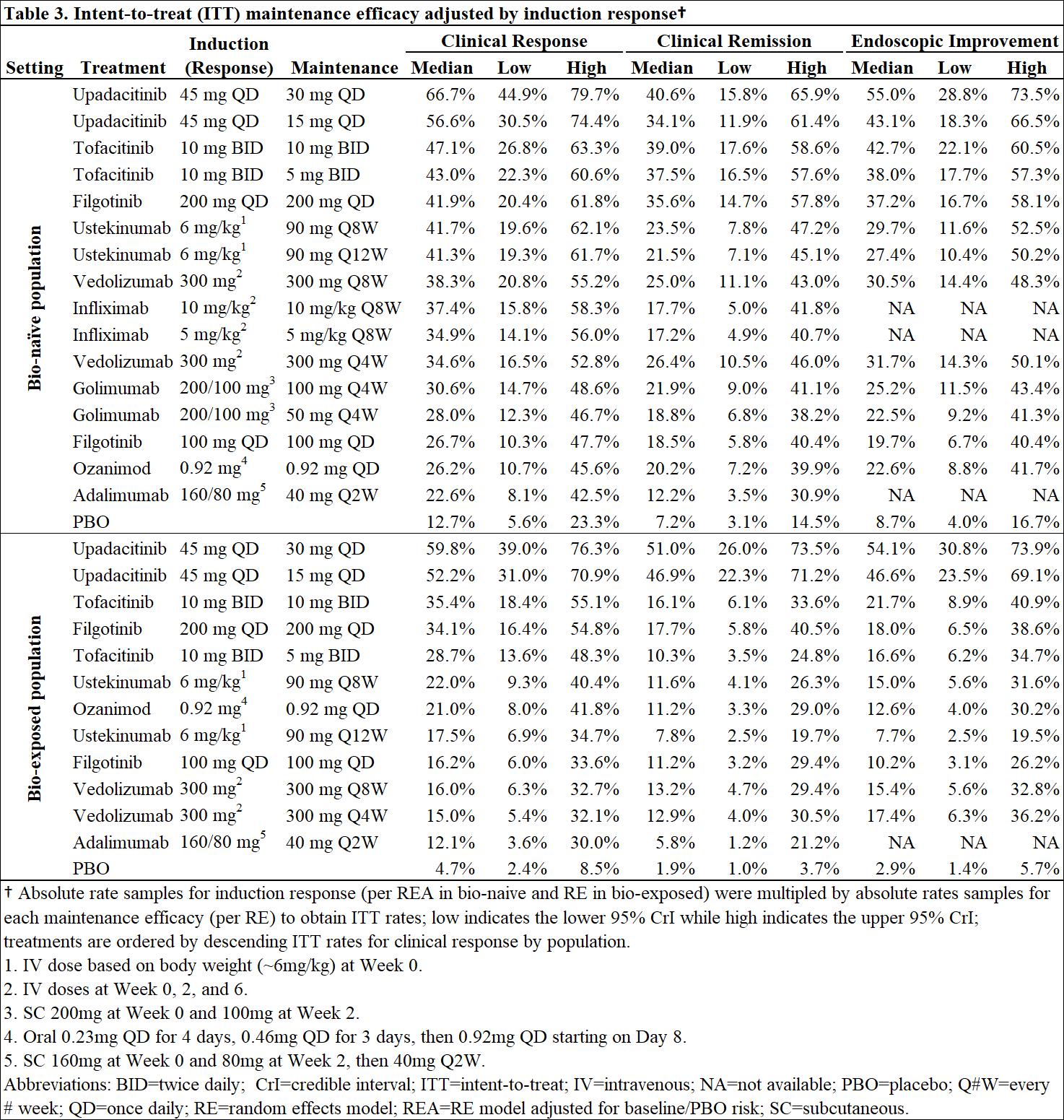
Efficacy and safety of advanced induction and maintenance therapies in patients with moderately to severely active Ulcerative Colitis: An indirect treatment comparison using Bayesian network meta-analysis
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Efficacy and safety of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in refractory perianal fistulae in Crohn’s Disease: Results from a prospective monocentric study
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Efficacy and safety of combination induction therapy with guselkumab and golimumab in participants with moderately-to-severely active Ulcerative Colitis: Results through week 12 of a phase 2a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter, proof-of-concept study
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Efficacy and safety of deucravacitinib, an oral, selective tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, in patients with moderately-to-severely active Ulcerative Colitis: 12-week results from the Phase 2 LATTICE-UC study
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM