Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
OP18: Surgical prevention of anastomotic recurrence by excluding mesentery in Crohn's Disease: The SuPREMe-CD Study
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP18: Treatment of perianal fistulas in Crohn’s Disease: Surgical closure after anti-TNF induction treatment versus anti-TNF without surgery (PISA II) - A patient preference RCT
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP19: Disease course and treatment outcomes of early resected Crohn's Disease patients: A Danish nationwide cohort study from 1997 to 2015
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP19: Extended mesenterectomy is not superior to mesenteric sparing resection in primary ileocolic resection for Crohn’s Disease in terms of postoperative endoscopic recurrence – results of an international randomised controlled trial
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP19: Gaps between ECCO quality standards of care and the real world: the E-QUALITY survey
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP19: Perinatal factors do not affect paediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease risk: A Scottish nationwide cohort study using administrative health data 1981-2017
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP20: Postoperative endoscopic recurrence after resection of Crohn’s terminal ileitis with Kono-S or side-to-side functional end anastomosis: results of a Multicenter Prospective Randomized Trial
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
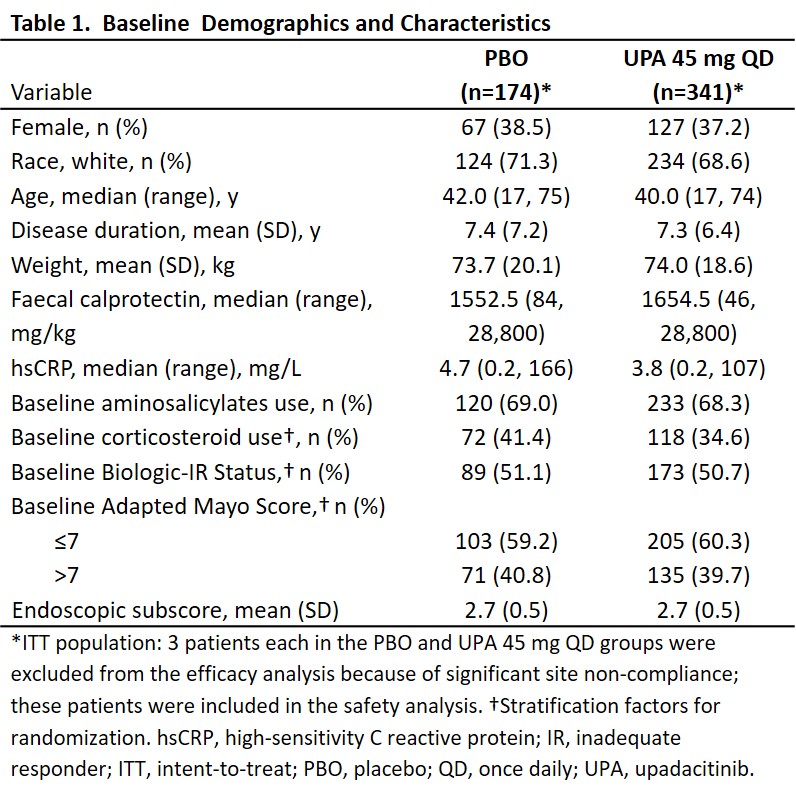
OP20: The effects of upadacitinib on ulcerative colitis symptom resolution and fatigue normalization in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: Phase 3 U-ACHIEVE and U-ACCOMPLISH results
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP21: COVID-19 morbidity/mortality and vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Poland: Nationwide Data
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP21: Positivity thresholds of a total infliximab and adalimumab anti-drug antibody assay: The prevalence of clearing and transient anti-drug antibodies in a national therapeutic drug monitoring service
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP21: Predictive value of Milan Ultrasound Criteria in Ulcerative Colitis: A prospective observational cohort study
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP21: Spatial Transcriptomics of Pre-treatment Biopsies Revealing Molecular Maturation State and Chronic Crypt Damage, Reflecting Histological Severity, as Predictors of Primary Responsiveness to TNF-α Inhibitors in Bio-naive Ulcerative Colitis Patients
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP22: Factors independently associated with fatigue in IBD: Results from the baseline dataset of the PREdiCCt study
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP22: The risk of cancer in pediatric-onset immune-mediated inflammatory diseases – a nationwide Danish study from 1980-2018.
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP22: Topical Sphingosine-1-Phosphate (S1P) Receptor 1 Modulation Regulates Gut Angiogenesis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP23: Asymptomatic inflammatory bowel disease diagnosed during the colorectal cancer population screening in Catalonia
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP23: Efficacy and safety of upadacitinib as induction therapy in patients with Moderately to Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Results from phase 3 U-ACCOMPLISH study
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP23: Efficacy and safety of vedolizumab SC in patients with Moderately to Severely active Crohn’s Disease: Results of the VISIBLE 2 study
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP23: Guselkumab induction restores intestinal immune homeostasis and promotes epithelial repair in moderately to severely active Ulcerative Colitis
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP24: A novel subcutaneous infliximab (CT-P13): 1-year results including switching results from intravenous infliximab (CT-P13) in patients with active Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
 Conclusion
Conclusion