Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
OP35: Efficacy of mirikizumab in comparison to ustekinumab in patients with moderate to severe Crohn’s disease: Results from the phase 3 VIVID 1 study
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP35: Treatment outcomes of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the biological era – A nationwide retrospective cohort study in three Nordic countries: Results from the TRINordic study
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP36: Investigating the role of bioactives produced by gut bacteria to modulate immune response in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP36: Real-world evidence on comparative effectiveness of Ustekinumab vs anti-TNF in Crohn’s disease with propensity score adjustment: two-year maintenance phase results from the prospective observational RUN-CD study
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP36: Risankizumab therapy induces improvements in endoscopic endpoints in patients with Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease: Results from the phase 3 ADVANCE and MOTIVATE studies
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP36: Risankizumab Versus Ustekinumab for the Achievement of Clinical Outcomes and Symptom Improvement in Patients With Moderate To Severe Crohn’s Disease: Results From the Phase 3b SEQUENCE Trial
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP37: Effect of the HLA-DQA1*05 allele on the efficacy of ustekinumab in patients with Crohn's Disease. Multicenter study based on the ENEIDA registry of GETECCU.
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP37: Is the withdrawal of anti-tumour necrosis factor in inflammatory bowel disease patients in remission feasible without increasing the risk of relapse? Results from the randomised clinical trial of GETECCU (EXIT)
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP37: Rapidity of symptom improvements during filgotinib induction therapy in patients with Ulcerative Colitis: Post hoc analysis of the phase 2b/3 SELECTION study
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP38: Developing a Cost-Effective Genomic Biomarker of Cancer Risk in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis using Low-Pass Whole Genome Sequencing of Unselected Endoscopic Biopsies: A Case-Control Study
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP38: Modulation of the septin cytoskeleton ameliorates intestinal fibrogenesis
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP38: Should all patients with newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel diseases be screened for metabolic bone disease? Results from a Danish population-based inception cohort study
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
OP38: Top-down infliximab superior to step-up in children with Moderate-to-Severe Crohn’s Disease – A multicenter randomized controlled trial
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP39: Safety of ustekinumab in IBD: Final pooled long-term safety analysis through 5 years in CD and 4 years in UC
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP39: The effect of phenotype and genotype on the plasma proteome in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP39: Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis with AMT-101, a novel oral Interleukin-10 Immunomodulatory fusion biologic that traffics across intestinal epithelium
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
OP39: Vedolizumab response in ulcerative colitis associates with reduced IgG+ plasma cells and FcγR signaling
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM
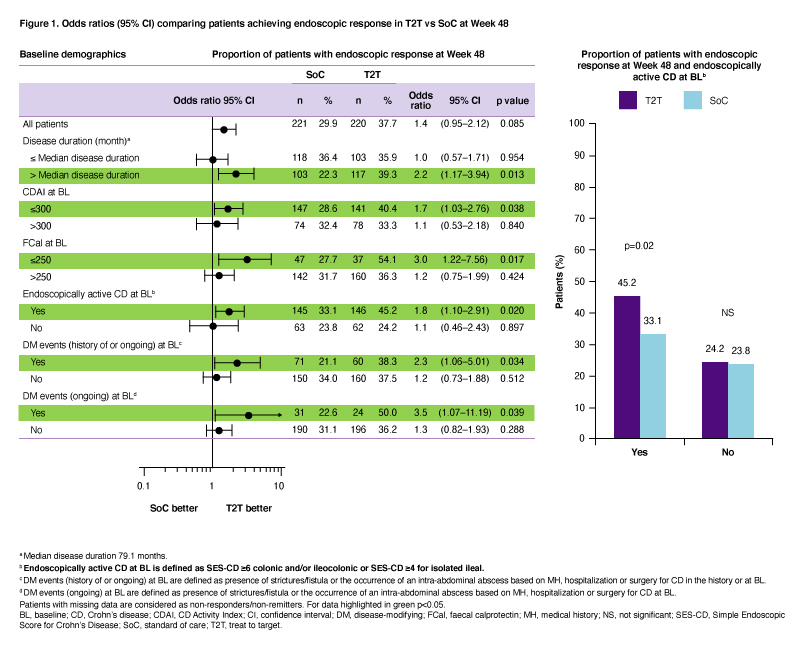
OP40: Analysis of clinical features associated with favourable outcomes from ustekinumab treat-to-target strategy in Crohn’s Disease patients in the STARDUST trial
2021
ECCO'21 Virtual
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
OP40: PRA023 Demonstrated Efficacy and Favorable Safety as Induction Therapy for Moderately to Severely Active UC: Phase 2 ARTEMIS-UC Study Results
2023
ECCO’23 Copenhagen
Friday, 14 July 2023, 2:22 PM
OP40: Transcriptomic signature of response to vedolizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe ulcerative colitis: Results from an international, multicentre, retrospective cohort study
2024
ECCO'24 Stockholm
Tuesday, 30 April 2024, 5:03 PM