Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
Perianal fistulas are characterised by expansion of interleukin-22 producing invariant natural killer T-cells and CD4+ T-cells which drive dysregulation of the extracellular matrix
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Perineal sinus after total coloproctectomy for CD: How to prevent? How to treat?
2021
10th S-ECCO IBD Masterclass
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
Perineal ultrasound
2021
8th ECCO Ultrasound Workshop - Advanced in collaboration with ESGAR
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
Perioperative pathway of care in IBD patients
2021
10th S-ECCO IBD Masterclass
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
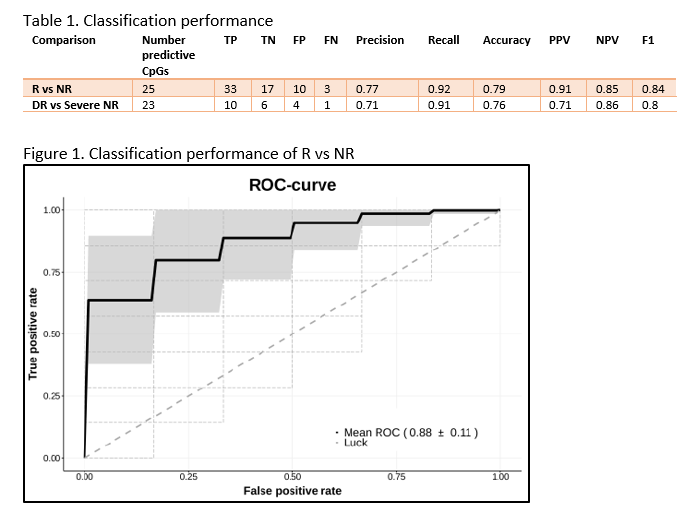
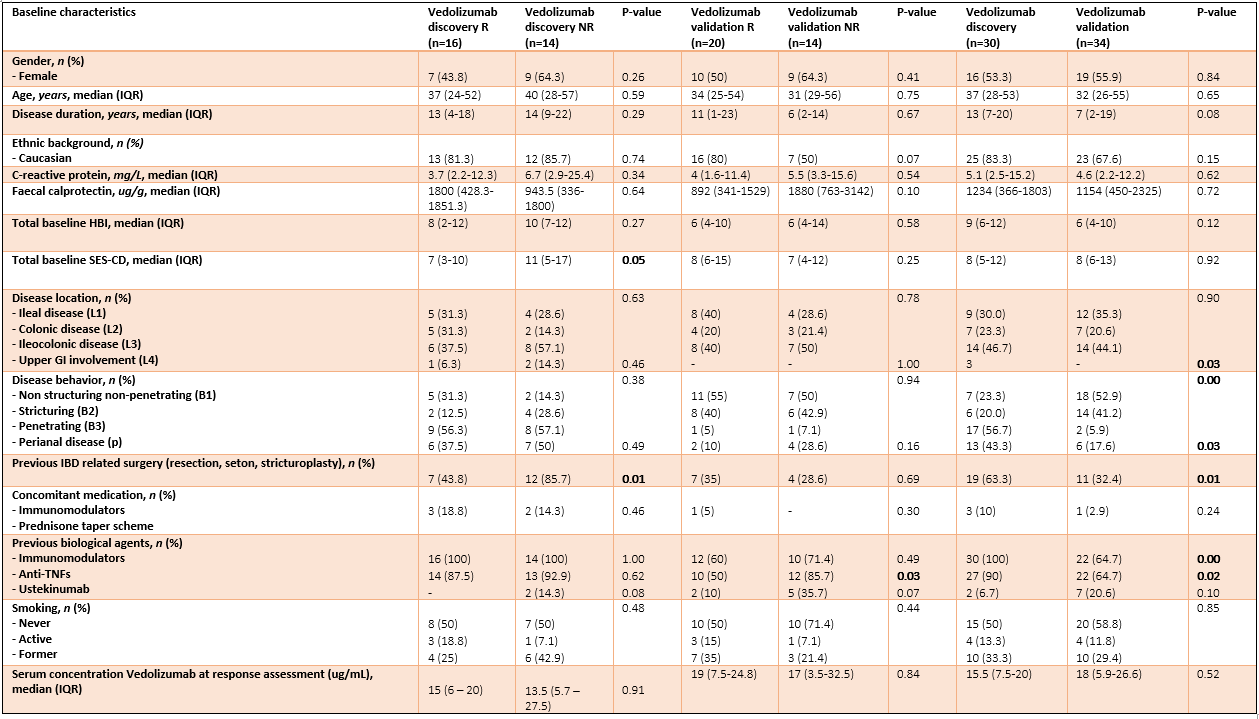
Peripheral blood DNA methylation biomarkers accurately predict clinical- and endoscopic response to vedolizumab in a real-life cohort of Crohn’s Disease patients
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Personalised medicine: Dream or reality?
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 1:56 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
Personalising Therapy
2018
Educational Audio Podcast
Friday, 28 February 2020, 3:47 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Friday, 13 January 2023, 12:20 PM by ECCO Administrator
Personalized nutrition in IBD - Are we there yet?
2021
6th D-ECCO Workshop
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
Personalized prediction: Statistician or algorithm? (Tandem Talk)
2021
4th School for Clinical Trialists
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
Pharmacoepidemiological studies on IBD using national registries. Examples from France
2018
4th EpiCom Workshop
Friday, 23 March 2018, 12:23 PM
1
Pharmacoepidemiology of distinct populations: a focus on ageing and ethnic populations
2018
4th EpiCom Workshop
Friday, 23 March 2018, 12:23 PM
1
Phenotypic and genetic determinants of medication response in patients in the UK IBD BioResource
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
Pits and pearls of Big Data in scientific research: Computational analysis, deconvolution, machine learning and more
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
Placing new molecules in the treatment pathway
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 1:46 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
Population level data on the incidence and complications of perianal Crohn’s disease
2020
JCC Podcast
Tuesday, 13 October 2020, 4:01 PM by Dauren Ramankulov
Positioning therapeutic strategies in IBD
2021
19th IBD Intensive Course for Trainees
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM