Exabis Library
Welcome to the e-CCO Library!
The elderly patient with IBD: Should azathioprine ever be used in the elderly? Should the type of surgery be different in an elderly patient?
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:02 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The first virtual chromoendoscopy artificial intelligence system to detect endoscopic and histologic remission in Ulcerative Colitis
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The forgotten populations in the gut
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:00 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The future of using nutrition to alter the microbiome
2021
6th D-ECCO Workshop
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
The ileorectal anastomosis in UC: Time for a comeback?
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:46 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The implementation of prognostic factors to manage and modify outcomes - case based discussion
2022
6th EpiCom Workshop
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The importance of the multidisciplinary team (MDT) and its impact on quality of life and medication adherence in patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
2022
16th N-ECCO Network Meeting
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The influence of different prednisolone tapering algorithms on the effectiveness of infliximab in patients with Ulcerative Colitis – A real-world cohort study
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The long-term safety outside clinical trials
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:50 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The MIND study: Assessment of psychological characteristics and postop outcomes
2021
10th S-ECCO IBD Masterclass
Friday, 1 October 2021, 12:41 PM
The multi-refractory paediatric patients: Out of the box therapeutic treatments
2020
ECCO'20 Vienna
Tuesday, 23 June 2020, 5:40 PM
The patient with psychological comorbidities: How to wean off opiates in these patients? Is there any preference in drugs?
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:18 PM by ECCO Administrator
1
The reproductive phase: Practical recommendations
2019
Scientific Programme
Wednesday, 5 June 2019, 9:01 PM
The tough get going – refractory IBD
2022
9th P-ECCO Educational Course - Paediatric IBD: When the going gets tough
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The use and efficacy of biological therapies 2010-2020 for Inflammatory Bowel Disease in a Danish tertiary centre
2022
ECCO'22 Virtual
Tuesday, 24 May 2022, 8:13 PM
The use of dietary therapy in IBD
2017
Talking Heads
Friday, 22 February 2019, 3:53 PM by ECCO Administrator
Friday, 13 January 2023, 11:33 AM by ECCO Administrator
The use of IBD medicine in patients with cancer: Which treatment should be stopped when cancer is diagnosed? Which treatment to use in a patient with a prior diagnosis with cancer?
2017
ECCO'17 Barcelona
Wednesday, 15 March 2017, 2:05 PM by ECCO Administrator
1



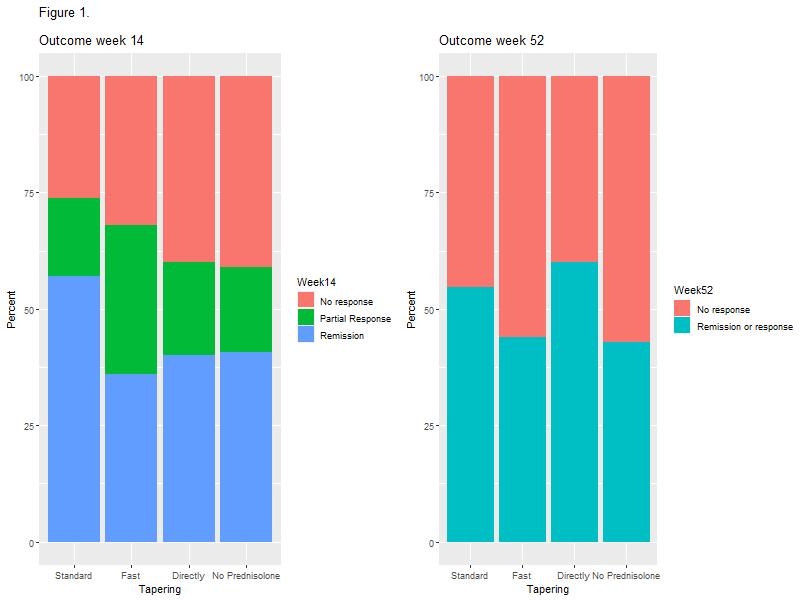
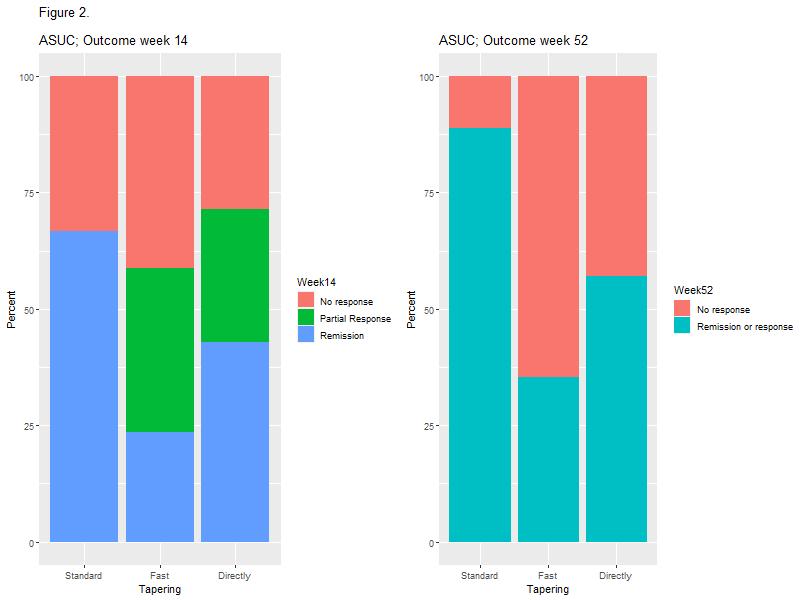
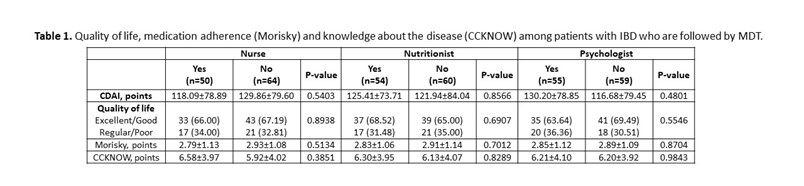 In total, 69 (60.53%) patients with CD and 45 (39.47%) patients with UC were included. The mean age was 39.16 (±13.50) years and 58.77% were female. The disease duration was 9.88 (±7.35) years. Presence of comorbidities was observed in 52.63% patients. About 57 (82.61%) patients with CD use biological therapy, with a statistical difference (p <0.0001) when compared to patients with UC (37.78%). The gastroenterologist was considered very important by 91.23% of patients, coloproctologist by 62.07% of patients, nurse by 65.05% of patients, nutritionist by 50% of patients and psychologist by 47.25% of patients. In the analysis of QoL, 24 (21.05%) patients had excellent QoL, 52 (45.61%) had good QoL, 29 (25.44%) had regular QoL and 9 (7.89%) had poor QoL, with no difference between patients who followed with nurses or other MDT professionals (Table 1). Medication adherence was low in 58.88% of patients. Knowledge about the disease was low (6.21 ± 3.99 points), being higher among patients with CD (p = 0.01). Patients identify the doctor as the main provider of care for their health, but about 10% leave with doubts from their appointments. 10% of patients think that more care with the nurse is necessary and less than 10% of patients are clarified by the nurse about QoL, ostomies, fecal incontinence, disease activity, biological therapy and sexuality.
In total, 69 (60.53%) patients with CD and 45 (39.47%) patients with UC were included. The mean age was 39.16 (±13.50) years and 58.77% were female. The disease duration was 9.88 (±7.35) years. Presence of comorbidities was observed in 52.63% patients. About 57 (82.61%) patients with CD use biological therapy, with a statistical difference (p <0.0001) when compared to patients with UC (37.78%). The gastroenterologist was considered very important by 91.23% of patients, coloproctologist by 62.07% of patients, nurse by 65.05% of patients, nutritionist by 50% of patients and psychologist by 47.25% of patients. In the analysis of QoL, 24 (21.05%) patients had excellent QoL, 52 (45.61%) had good QoL, 29 (25.44%) had regular QoL and 9 (7.89%) had poor QoL, with no difference between patients who followed with nurses or other MDT professionals (Table 1). Medication adherence was low in 58.88% of patients. Knowledge about the disease was low (6.21 ± 3.99 points), being higher among patients with CD (p = 0.01). Patients identify the doctor as the main provider of care for their health, but about 10% leave with doubts from their appointments. 10% of patients think that more care with the nurse is necessary and less than 10% of patients are clarified by the nurse about QoL, ostomies, fecal incontinence, disease activity, biological therapy and sexuality.